Did you ever wonder what happens to the waste that comes from wood processing? From sawmills to furniture manufacturers, the wood processing industry inevitably generates a substantial amount of waste. The waste can include everything from wood chips and sawdust to bark and shavings. But what exactly is done with all this waste? In this article, we will explore the different methods of managing and repurposing the waste produced by wood processing, highlighting the importance of sustainable practices in this industry. So, let’s delve into the world of wood processing waste and discover the hidden potential behind it!
Wood chips
Definition of wood chips
Wood chips are small pieces of wood that are obtained from various sources during the process of wood processing. These chips are typically derived from the outer layers of logs or from the residual wood that is generated while manufacturing wood products.
Sources of wood chips
Wood chips can be obtained from a variety of sources. One common source is forestry operations, where trees are harvested and processed into lumber. In these operations, the branches, bark, and other parts of the tree that are not suitable for making lumber are often chipped. Another source is the wood processing industry, where logs are transformed into various products such as furniture, flooring, and paper. During this process, wood chips are generated as a byproduct.
Uses of wood chips
Wood chips have a wide range of uses in various industries. One major use is as a fuel source for biomass energy production. Wood chips can be burned in specially designed boilers to generate heat and electricity. They can also be used as a raw material for the production of paper and paperboard. Additionally, wood chips are commonly used for landscaping purposes, such as mulching flower beds and gardens. They can also be used for animal bedding or as a component of compost.
Disposal of wood chips
The disposal of wood chips depends on their quality and intended use. If the wood chips are clean and free from contaminants, they can be recycled or reused in various ways. For instance, they can be utilized as mulch in landscaping or sent to facilities that produce wood-based products. However, if the wood chips are contaminated with chemicals or other substances, they may need to be disposed of in a designated landfill or incinerated in a controlled environment to prevent environmental contamination.
Sawdust
Definition of sawdust
Sawdust refers to the small particles or shavings of wood that are produced when wood is cut, shaped, or sanded. It is a byproduct of various woodworking processes and is commonly found in woodworking shops and factories.
Sources of sawdust
Sawdust is primarily generated in sawmills, carpentry workshops, and furniture manufacturing facilities. During the cutting or shaping of wood, saws and other woodworking tools produce small particles of wood, which accumulate as sawdust. It can also be produced in smaller quantities from DIY woodworking projects at home.
Uses of sawdust
Sawdust is a versatile material with numerous uses across different industries. One of the main applications is as a bedding material for livestock, such as poultry, rabbits, and horses. It provides a comfortable and absorbent surface for animals. Sawdust is also commonly used as a component of wood-based panels and boards, such as particleboard and medium-density fiberboard (MDF). Additionally, it can be utilized as a moisture-absorbent material in packaging, especially for delicate items that require protection during transportation.
Disposal of sawdust
The disposal of sawdust can be done in an environmentally responsible manner. One option is to recycle it by incorporating it into compost or using it as a mulch for gardening. Sawdust that is untreated and free from contaminants can also be burned as a source of biomass energy. However, it is important to note that sawdust generated from woodworking processes that involve the use of chemical treatments or preservatives may require special handling and disposal procedures to prevent environmental harm.
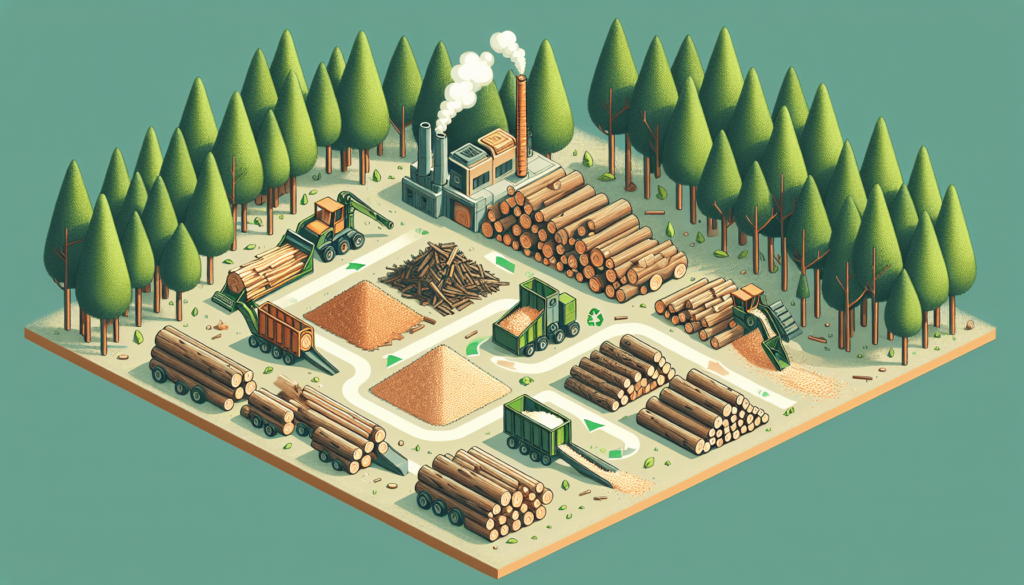

Wood shavings
Definition of wood shavings
Wood shavings are thin, elongated pieces of wood that are produced by shaving or planing the surface of a larger piece of wood. They are commonly generated during woodworking processes that involve shaping or finishing wood.
Sources of wood shavings
Wood shavings are primarily obtained from woodworking operations, such as carpentry workshops, sawmills, and furniture manufacturing facilities. When wood is planed or shaved to achieve a smooth surface or a specific shape, the thin shavings that are produced are collected as wood shavings.
Uses of wood shavings
Wood shavings have diverse uses across various industries. One significant application is as bedding material for animals, particularly in livestock farming and equestrian settings. They provide a soft and comfortable surface for animals to rest on while also aiding in moisture absorption. Additionally, wood shavings can be utilized as a packaging material to protect fragile items during shipment. In gardening, wood shavings are often used as mulch to retain moisture in the soil and inhibit weed growth. Wood shavings can also be processed into composite materials or used as fuel in biomass energy production.
Disposal of wood shavings
The disposal of wood shavings largely depends on their quality and potential contaminants. Clean wood shavings can be repurposed or recycled for various applications. For example, they can be used as animal bedding or incorporated into compost. If the wood shavings are contaminated with chemicals or other substances, proper disposal methods must be followed to prevent environmental contamination. This may involve sending them to designated waste disposal facilities or utilizing incineration methods that meet environmental regulations.
Bark
Definition of bark
Bark refers to the protective outer layer of a tree trunk. It acts as a shield, defending the tree against external elements, such as insects, diseases, and mechanical damage. Bark is made up of various layers, including the cork cambium, phloem, and outer bark.
Sources of bark
Bark is primarily obtained from trees that are being processed for timber or other wood products. During the initial stages of logging, the bark is stripped from the trees and separated from the usable timber. Bark can also be obtained as a byproduct of sawmills and wood processing facilities, where it is removed from logs before further processing.
Uses of bark
Bark has several practical uses, particularly in the horticultural and agricultural sectors. It is commonly used as mulch for plants and trees to retain moisture in the soil, regulate temperature, and suppress weed growth. Bark can also be processed into mulch mats or chips that provide erosion control in landscaping projects. Additionally, certain types of bark, such as cork, are harvested for commercial purposes and used in various industries, including flooring, insulation, and wine production.
Disposal of bark
The disposal of bark largely depends on its condition and intended use. If the bark is clean and free from contaminants, it can be repurposed or recycled for mulching, composting, or other landscaping applications. However, if the bark is infested with pests or diseased, it is important to follow proper disposal procedures to prevent the spread of pests and diseases. This may involve sending the bark to designated waste management facilities or utilizing controlled incineration methods.

Wood fines
Definition of wood fines
Wood fines are finely ground or pulverized wood particles that are generated during wood processing operations. They are typically obtained from residual wood materials such as sawdust, bark, or wood chips.
Sources of wood fines
Wood fines can be obtained from various sources within the wood processing industry. They are often derived from processes that involve the grinding or pulverizing of wood materials to achieve a desired texture or consistency. This includes operations such as milling, chipping, or grinding of wood products.
Uses of wood fines
Wood fines have a range of potential uses across different industries. They can be utilized as a raw material in the production of wood-based panels, such as particleboard or oriented strand board (OSB). Wood fines can also be processed into biomass fuel pellets or briquettes for energy generation. In the agricultural sector, wood fines can be incorporated into compost or used as a soil amendment to enhance fertility and moisture retention.
Disposal of wood fines
The disposal of wood fines largely depends on their quality and intended applications. If the wood fines are clean and uncontaminated, they can be recycled and used for various purposes. For instance, they can be incorporated into composite materials, composted, or utilized as a fuel source. However, if the wood fines are contaminated with chemicals or other substances, special care must be taken to ensure proper disposal. This may involve sending them to designated waste management facilities or utilizing controlled combustion methods.
Logging residue
Definition of logging residue
Logging residue refers to the non-commercial byproducts and residual materials that are left behind during the process of timber harvesting. It comprises branches, tree tops, and other debris that are not suitable for commercial use.
Sources of logging residue
Logging residue is primarily generated during forest harvesting operations. When trees are cut down for timber production, the branches, tree tops, and other parts that are not used for commercial purposes are considered logging residue. This residue is a natural outcome of sustainable forestry practices aimed at maximizing the utilization of the harvested trees.
Uses of logging residue
Logging residue can be put to various uses across different industries. One significant application is the production of biomass energy. The residue can be utilized as a feedstock for biomass power plants, where it is burned to generate heat and electricity. Logging residue can also be used as a raw material in the production of wood pellets or briquettes for residential heating or industrial processes. Additionally, it can be processed into pulp for paper and cellulose-based products.
Disposal of logging residue
The disposal of logging residue is typically done in an environmentally responsible manner. It is often utilized as a valuable resource rather than being disposed of as waste. The residue can be sent to facilities that specialize in biomass energy production, where it is used as fuel. When not used for energy purposes, logging residue can be left on the forest floor to decompose naturally, contributing to nutrient cycling and ecosystem health. Proper management and disposal practices ensure minimal waste and environmental impact.
Wood ash
Definition of wood ash
Wood ash is the residue that remains after the combustion of wood, typically in a fireplace, wood stove, or biomass power plant. It consists of the inorganic components of wood that are not consumed during the burning process.
Sources of wood ash
Wood ash is primarily derived from the burning of wood in various settings. It can be obtained from residential sources, such as fireplaces and wood stoves, where wood is burned for heating purposes. Wood ash can also be generated in industrial settings, particularly in biomass power plants where wood-based biomass is burned to generate heat and electricity.
Uses of wood ash
Wood ash has a range of potential uses across different industries and applications. In agriculture, it can be utilized as a soil amendment to enhance soil fertility and pH balance. Wood ash contains nutrients such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which can benefit plant growth. Additionally, wood ash can be used in the production of cement or as a component in the manufacturing of soap or cleaning products. It can also serve as a natural deodorizer or abrasive cleaner in household settings.
Disposal of wood ash
The disposal of wood ash depends on its quality and any potential contaminants. If the wood ash is free from pollutants and chemical additives, it can be safely incorporated into compost or used as a soil amendment in gardening and agriculture. It is important to follow proper guidelines and recommendations regarding the application of wood ash to ensure optimal benefits and prevent negative impacts on plant health. However, if the wood ash is contaminated or mixed with hazardous substances, it may need to be disposed of in designated waste management facilities to prevent environmental harm.
Steam
Definition of steam
Steam is the gaseous form of water that is produced when water is heated to its boiling point and vaporizes. It is an invisible gas that consists of tiny water droplets suspended in the air.
Sources of steam
Steam can be produced from various sources depending on its intended applications. In industrial settings, steam is commonly generated by burning fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, or oil, in boilers. The combustion process heats water and produces steam under high pressure. Steam can also be generated through the use of renewable energy sources, such as biomass or geothermal energy. Additionally, steam can be obtained by utilizing solar thermal energy or by utilizing waste heat from industrial processes.
Uses of steam
Steam has numerous applications across different industries and everyday life. One of the major uses is in power generation, where steam turbines are used to convert the heat energy of steam into mechanical energy, which then drives generators to produce electricity. Steam is also extensively used in industrial processes, such as heating, sterilization, and cleaning. In residential settings, steam is utilized for heating and cooking, such as in steam ovens or humidifiers. Additionally, steam is utilized in various mechanical systems, including steam engines, locomotives, and steam-powered vehicles.
Disposal of steam
Steam, being a gaseous state of water, does not require specific disposal methods. Once steam is utilized and its heat energy is converted into mechanical energy or work, it condenses back into water form. This condensed water can be recovered, treated if necessary, and reused in various applications, such as irrigation or industrial processes. Proper management and recycling of water is crucial to ensure efficient use of resources and minimize water wastage.
Green liquor
Definition of green liquor
Green liquor is a chemical solution that is produced during the Kraft pulping process, a method used in the production of pulp for paper and paperboard. It is a mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium sulfide, and other chemicals.
Sources of green liquor
Green liquor is primarily generated in the Kraft pulping process, which involves the cooking of wood chips with a combination of chemicals to break down the lignin and extract cellulose fibers. The resulting solution, known as black liquor, undergoes further processing to separate the green liquor, which contains the chemicals necessary for reuse in the pulping process.
Uses of green liquor
Green liquor plays a crucial role in the Kraft pulping process. It serves as a key component for the pulping liquor, which helps dissolve the lignin and separate the cellulose fibers from the wood chips. The dissolved lignin is removed, leaving behind the cellulose fibers that are further processed to produce pulp for paper and paperboard. Additionally, some of the chemicals present in the green liquor can be recovered and reused, contributing to the sustainability of the pulping process.
Disposal of green liquor
The disposal of green liquor is carefully managed to ensure the efficient reuse of chemicals and minimize environmental impact. In the Kraft pulping process, green liquor undergoes a series of chemical recovery steps to extract valuable components and reuse them in the pulping process. After the chemicals have been fully utilized and recovered, the remaining residue, known as weak black liquor, may undergo further treatment to extract additional chemicals or be processed in black liquor recovery boilers to generate steam and recover energy. The final disposal of any residual waste is typically conducted in accordance with relevant environmental regulations and considerations.
Black liquor
Definition of black liquor
Black liquor is a byproduct of the Kraft pulping process, which is used to produce pulp for manufacturing paper and paperboard. It is primarily composed of lignin, hemicellulose, and dissolved organic compounds.
Sources of black liquor
Black liquor is generated during the Kraft pulping process, a chemical-based method used to break down wood chips and separate the cellulose fibers for paper production. The wood chips are cooked in a solution of chemicals, which dissolves the lignin and other organic compounds, leaving behind the cellulose fibers. The resulting mixture, known as black liquor, is a viscous liquid with high organic content.
Uses of black liquor
Black liquor, despite being a byproduct of the pulping process, has significant value and utility. Its primary use is in the recovery of chemicals used in the pulping process. Through various chemical recovery processes, valuable components such as sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide are extracted from the black liquor and reused in the pulping process. Additionally, black liquor is often burned in specialized recovery boilers to generate steam and recover energy. This energy can be used for various purposes within the pulp and paper mill, reducing the reliance on external energy sources.
Disposal of black liquor
The disposal of black liquor is carefully managed to maximize resource recovery and ensure minimal environmental impact. The black liquor undergoes a series of chemical recovery processes to extract valuable components, which are then reused in the pulping process. The remaining weak black liquor or residual waste can be further processed, typically in black liquor recovery boilers, to generate steam and recover energy. This energy can offset the energy requirements of the pulp and paper mill. Any residual waste that cannot be utilized or recovered is disposed of in accordance with applicable environmental regulations to prevent environmental contamination.

Hi, I’m James Gheen, the creator behindWoodRebirth.com. As someone passionate about sustainability and environmental stewardship, I created this pioneering online platform to change how we approach wood waste and pallet disposal. Through detailed recycling and disposal guides, creative DIY projects, and upcycling inspirations, I aim to inspire individuals and businesses to adopt eco-friendly practices in their wood waste management. At WoodRebirth.com, we foster a vibrant community focused on education and engagement, encouraging the sharing of ideas and success stories. Join me in our mission to give wood waste a new lease on life, making a tangible impact on our environment, one pallet at a time.